In this article, we will go through the symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and treatment options for hirsutism.
What are the symptoms of hirsutism?
The symptoms would vary based on the severity of the condition and its underlying cause. However, here are some common symptoms of hirsutism found in most females –
- A woman, even with the mildest form of hirsutism, would notice significant growth of hair on various areas like the upper lip, chin, around the nipples, lower abdomen, or sideburn areas. These are the areas where hair growth is uncommon in females. The hair grows thicker, darker, and faster than normal in these areas.
- A more advanced stage of hirsutism will cause hair growth in other parts of the body like the shoulders, back, chest, and upper abdomen. This usually begins around puberty. If the symptoms start before or after puberty, then the cause would most likely be hormonal problems.
Apart from this, there could also be other symptoms like –
- An excessive production of androgen (the primary cause of hirsutism), which will lead to acne and oily skin.
- Hirsutism is also caused due to hormonal imbalance, which can result in infertility.
- A deeper voice
- Enlarged clitoris
- A receding hairline
- Increased muscle mass
- Decreased breast size
- Hair loss
What are the causes of hirsutism?
There can be various causes of hirsutism, but here are a few common ones –
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS): The most common cause of hirsutism is PCOS. It is a hormonal disorder that affects the ovaries. It starts during puberty and causes an imbalance of sex hormones. PCOS leads to excessive androgen production in the body, which ultimately results in hirsutism.
- Congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH): This genetic disorder affects the adrenal glands, leading to an overproduction of hormones like androgen and cortisol. This will result in hirsutism in women.
- Cushing’s syndrome: Cushing’s syndrome is a rare disorder that happens when the body is exposed to high levels of cortisol. It might develop from the adrenal gland or from taking too many steroidal medications for a long time. Excess cortisol can cause hormonal imbalances, including increased androgen production and hirsutism.
- Tumors: Though rare, few ovarian or adrenal gland tumors can secrete androgens, causing hirsutism.
- Medications: Certain medications (such as anabolic steroids or medications used to treat endometriosis, Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA), or testosterone) can cause hirsutism in women. The hirsutism can also be caused from skin to skin contact if your partner uses topical products containing androgen.
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese can lead to increased androgen production, which can cause hirsutism.
- Insulin resistance: Insulin resistance, which is commonly associated with PCOS, can cause hirsutism in women.
- Hypothyroidism: An underactive thyroid gland can lead to hormonal imbalances and hirsutism.
- Congenital disorders: Rare congenital disorders such as McCune-Albright syndrome and ovarian hyperthecosis can cause hirsutism in women.
- Ancestry: Women who are from certain parts of the world, like the Mediterranean, South Asia, and the Middle East, are more likely to have body hair with no identifiable cause.
- Family history: Various conditions that are responsible for hirsutism, like polycystic ovary syndrome and congenital adrenal hyperplasia, often run in families.
- Idiopathic hirsutism: In some cases, the cause of hirsutism may not be identified, and it is referred to as idiopathic hirsutism. This form of hirsutism is typically mild and can be managed with hair removal techniques.
How is hirsutism diagnosed?
The diagnosis of hirsutism typically involves multiple steps starting from understanding the patient’s medical history to physical examination and laboratory tests. Let us go through these steps in detail –
- Medical History – Initially, the dermatologist will take a look at your medical history with a primary focus on the menstrual cycle. If the patient has a regular menstrual cycle, then the cause could be genetics. So the dermatologist will check the family history and medications. If the dermatologist finds that the menstrual cycle is irregular, then the cause would most likely be Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).
- Physical Examination – The dermatologist will then conduct a physical examination to assess the extent of the hair growth and its pattern on the face, chest, and back.
- Hormonal Testing – Various tests like blood tests, testosterone, dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate (DHEAS), luteinizing hormone (LH), follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) tests will be conducted to identify if the patient is suffering from PCOS, adrenal gland tumor, or ovarian tumors. If the test results indicate a high level of testosterone or androgen, then hormonal disorders will be the main cause.
Mild hirsutism (no other symptoms) is mainly due to the overproduction of androgen hormones. In that case, no further tests would be required.
- Imaging – The health care professional might also conduct some imaging studies, including an MRI scan of the brain, ultrasound of the ovaries, and CT scan of the adrenal glands to check for any abnormalities.
How is hirsutism treated?
Most of the treatments of hirsutism work by treating its underlying cause. Here are the different options you have –
Medications
The following medications take a minimum of 6 months to see any significant reduction in hair growth –
- Oral contraceptive – Hormonal contraceptives or birth control pills contain estrogen or progestin. They are quite effective in treating hirsutism caused by excess androgen production. They are given to women who aren’t planning to get pregnant. Side effects include mild headache or nausea.
- Anti-androgens – They are usually prescribed if the oral contraceptives are not effective. These medicines help in blocking the androgens from attaching to the receptors in the body. Side effects include menstrual irregularities.
- Topical Cream – There are facial creams that specifically work by slowing down the growth of facial hair in women. These creams are directly applied to the affected areas. Though it slows down the growth of new hair, it doesn’t get rid of the existing hair.
Home remedies
There are various home remedies that you can employ to temporarily remove or reduce the visibility of hair. These include –
- Plucking: This traditional method is fine if you are removing a few strands of hair, but it is not suitable for large patches of hair. This method is usually done using a tweezer, thin threads, or a device tailor-made for this purpose. Usually, the plucked hair grows back.
- Shaving: This is a quick and inexpensive way to remove unwanted hair from the face and other parts of the body. However, one must repeat the procedure regularly to maintain the results.
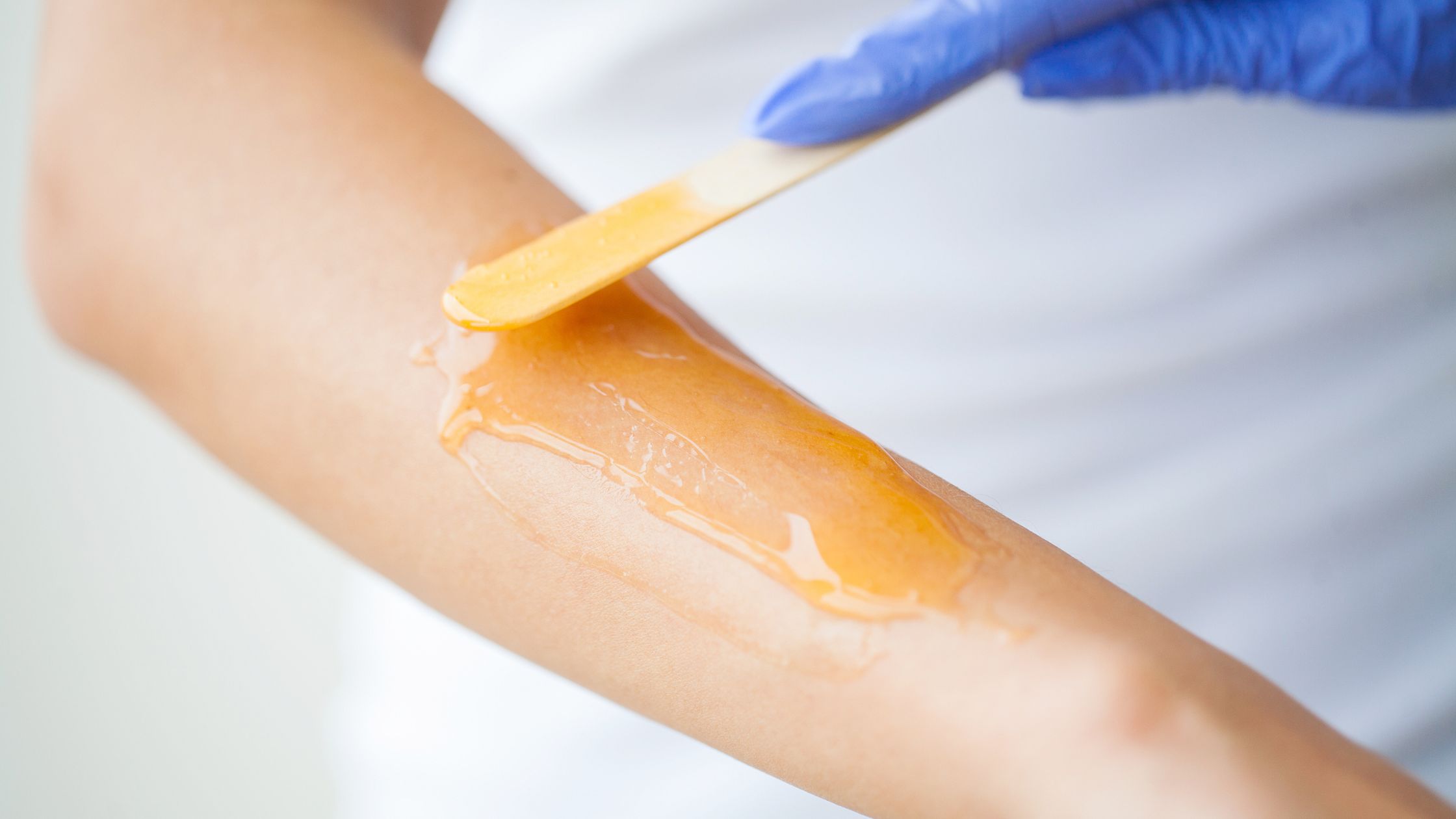
- Waxing: Wax is applied on the affected area first. Once it hardens, it is pulled away from the skin, which will remove the hair along with it. Waxing is ideal for removing hair from a large area. Your skin might temporarily sting. There can also be redness and swelling.
- Depilation: When you use chemical depilatories on the affected skin, it will dissolve the hair. They are available in various forms, such as gel, lotion, and cream. This procedure can irritate the skin and cause dermatitis.
- Bleaching: This can be a great option for people with light skin. Bleaching will lighten the color of the hair and make it less noticeable on people, especially the ones with light skin color. Hydrogen peroxide used on bleaching products can irritate, so it’s best to perform a patch test first.
Procedures
The results from the below procedures last longer than home remedies –
- Laser therapy – In this, a concentrated beam of laser is directed at the affected area of your skin. The laser will damage the hair follicles and prevent hair from growing. Multiple sessions will be required to achieve the desired results. Laser therapy is the best option for people with black, auburn, or brown hair.
People with dark skin or tanned skin must consult and talk to their dermatologist before opting for laser treatment. People with these skin types tend to experience different side effects from the treatment, such as blistering, inflammation, or lightening/darkening of the skin color when compared to the natural tone.
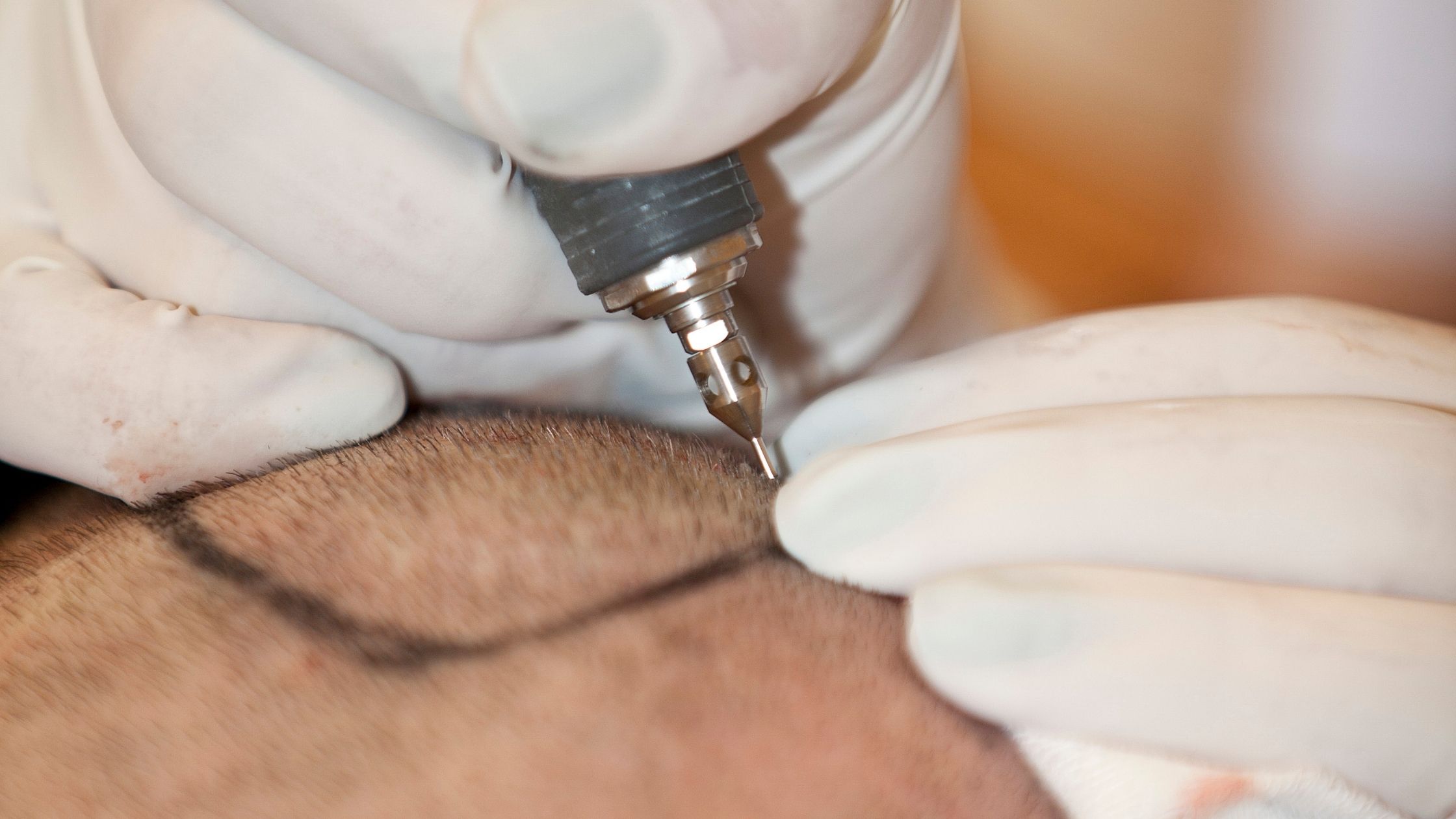
- Electrolysis – In this treatment, a small needle is inserted into each hair follicle, and an electric pulse is emitted from the needle. This will destroy the hair follicle. You will need multiple sessions to achieve the desired results. This treatment is best suited for people with natural white or blond hair. Electrolysis is a slightly painful procedure. So a numbing cream is usually applied on the affected skin to reduce discomfort.
Conclusion
It is not possible to treat hirsutism completely, but a nutritious diet and regular exercise can control hirsutism to a great extent. By supplementing it with a procedure like laser therapy, hair growth can be considerably reduced, improving the overall quality of life. But it is important to consult with a dermatologist to determine the best course of treatment for your needs. Book an appointment with Dr. Renu to control and treat your hirsutism.