The exact cause of melanoma is mostly unknown. But it is widely believed that skin exposure to UV rays, tanning beds, or lamps can increase the risk of melanoma. Like any other cancer, melanoma is curable through surgery if detected in the early stages.
Even though melanoma accounts for only 1% of all skin cancers, it is extremely lethal. In fact, the vast majority of deaths due to skin cancer are caused by melanoma. Also, it is quite common in young people (especially women under the age of 30).
The occurrence of Melanoma has been dramatically increasing over the past couple of decades, primarily due to climatic changes such as the increase in the intensity of UV rays.
What are the symptoms of melanoma?
Initial melanoma symptoms can look like this –
- Formation of an unusual growth on the skin or development of new pigments.
- Changes in the existing mole.
To understand the symptoms better, you need to understand the difference between a normal mole and moles that indicate melanoma.
Normal Moles
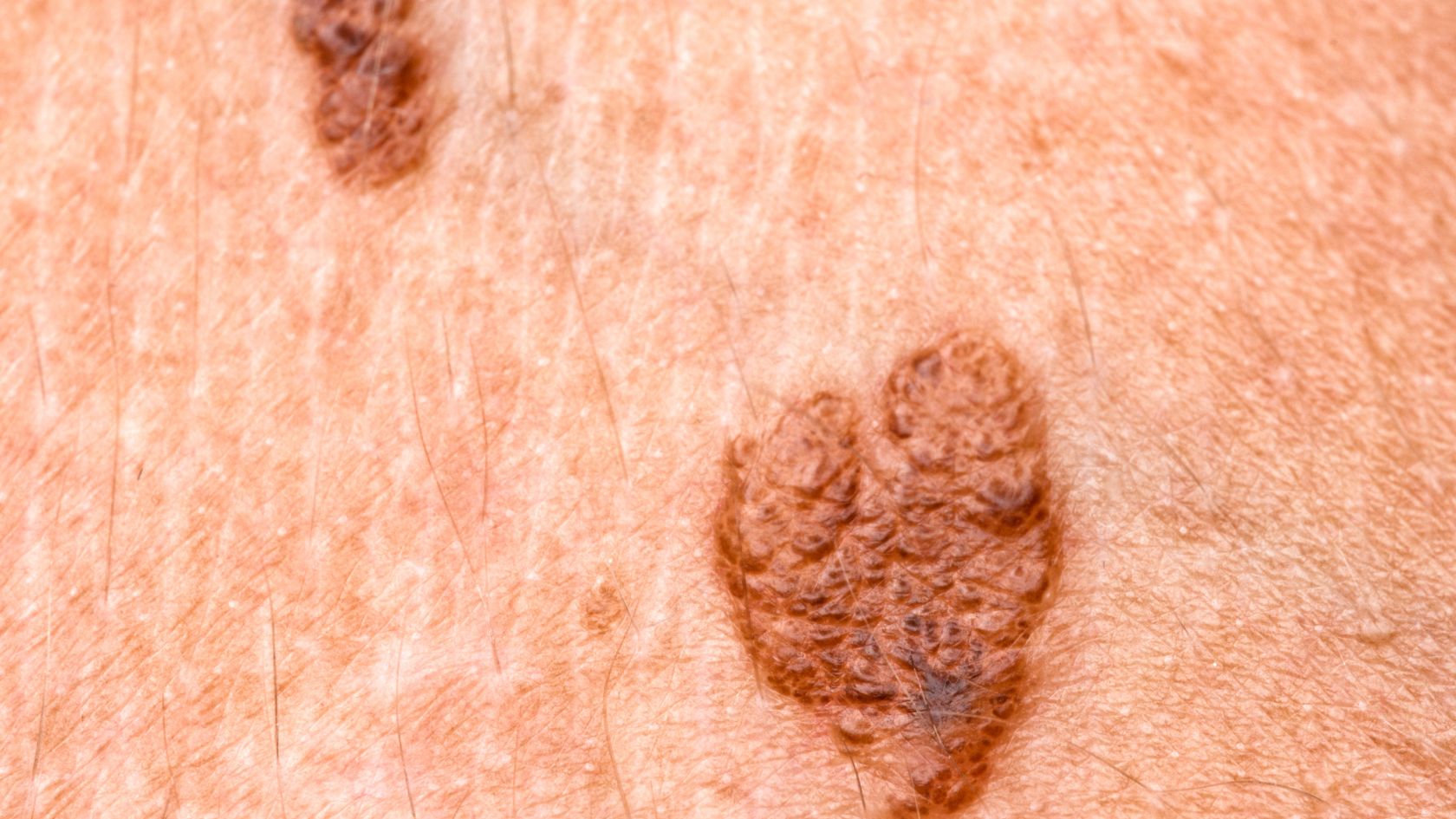
Most moles would be in a uniform color – it can be black, brown, or tan. The mole will also have a distinct border that separates it from the surrounding skin. It is usually oval or round in shape. The size of the mole would be about 6 millimeters in diameter, the same size as a pencil eraser.
Most of the moles on your skin are typically formed when you are young, while new moles can form up to the age of 40. The appearance of the mole can change over time and also few moles can completely disappear as you age.
Moles that might indicate melanoma
By using the English alphabets ABCDE you can identify a mole that is unusual and can indicate melanoma or any type of skin cancer. Here are they –
Asymmetry: First, look out for moles that have irregular shapes. For example, see if the mole that has two different appearing halves.
Border: A typical characteristic of a melanoma mole is that it will be scalloped, irregular, or have a notched border.
Color: Search your skin for growths that have an irregular and uneven distribution of colors.
Diameter: Next thing to look out for is the size of the mole. If you find the size of the mole to be greater than 6 millimeters in diameter, then it can be a melanoma or any other skin cancer.
Evolving: A cancerous mole will evolve over time, and you can notice changes in appearance, color, or size. Some moles can also evolve and develop new signs like itchiness or bleeding.
Causes of melanoma
As pointed out above, melanoma largely occurs due to exposure to UV rays. When the UV rays fall on the skin, it can damage its DNA. This would make changes to a particular gene that is responsible for the splitting and growth of cells. The problem would start when the cells get affected, damage your DNA, and start reproducing and forming a mass of cancerous cells.
Anyone can develop melanoma, but here are a few people who are at a higher risk of developing the disease:
- Family history of Melanoma
- Excess sun exposure
- History of tanning bed use
- A weakened immune system
- Personal history of melanoma
- Freckles, red hair, fair skin, blond or blue eyes
- Living in high elevations or near the equator can increase your risks of melanoma as these locations increase your UV exposure
- Presence of many moles, especially atypical moles
Melanoma can be commonly found in people with fair skin, but it can also occur in people of all skin colors and types. Usually, people with darker skin tones develop melanoma in hidden places like nails, palms, and soles.
Melanoma treatment
The treatment for melanoma would vary depending upon its stage and your general health. Here are the different treatment options –
Surgery
This treatment would involve a surgeon cutting out the cancerous skin and some healthy skin around it. The quantity of healthy skin that would be removed would be based on the location, color, and size of the skin cancer. The procedure would usually take place in the dermatologist’s office under local anesthesia. Advanced cases would require additional treatments apart from surgery.
Metastasectomy
This treatment is for people who have melanoma growths in their organs. The surgeon would remove melanoma bit-by-bit from the organs.
Immunotherapy
This is used to boost your immune system and help it to fight cancer on its own.
Lymphadenectomy
In certain cases where the melanoma has spread, the dermatologist will remove the lymph nodes from the primary site. This would help in preventing the spread of the virus to other parts of the body.
Radiation therapy
In this treatment, high-energy rays are used to target and attack the cancer cells to shrink the size of the tumor.
Targeted cancer therapy
Drugs are used to attack cancer cells. In this targeted approach, healthy cells are unharmed.
Conclusion
Melanoma is completely curable if identified at the early stages. If your family has a history of melanoma, then you should keep looking at your skin for any sudden changes or abnormal appearances. Apart from this, stay away from the sun and tanning beds. Use sunscreen regularly and try to cover your skin using hats, long sleeves, glasses, and pants whenever possible. You can also visit us to get a complete skin check every once a year. To book an appointment with us, click here.